Environmental Sustainability
Climate Action
ARIZON deeply understands the environmental, economic, social, and health challenges posed by climate change, and recognizes that addressing climate change is crucial for sustainable business operations. Since 2023, the Company has adopted the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD) framework issued by the Financial Stability Board to assess the impact of climate change on the Company, identify climate risks and opportunities, and mitigate and manage the impact of environmental change on the Company.
Governance
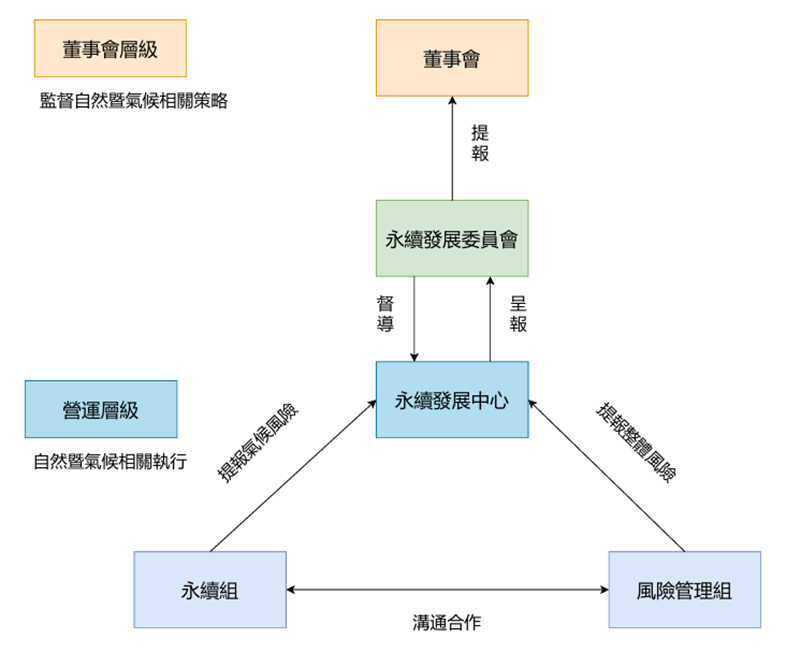
The Board of Directors has established a "Sustainability Committee" as a functional committee, chaired by the Chairman and composed of one director and three independent directors. This committee is responsible for overseeing the operation of the "Sustainability Center." The Center has several working groups, all coordinated and driven by senior executives from Yageo. The Sustainability Group leads the assessment of climate risks and opportunities and the formulation of strategies; the Risk Management Group maintains real-time horizontal communication with the Sustainability Group to ensure the Group's understanding and management of climate-related risk issues.
Under the chairman's leadership, senior management of each functional group holds working meetings from time to time to coordinate the work of business group and functional department members, and jointly promote risk assessment and internal management mechanisms for operations and climate issues.
In addition, the Executive Secretary of the Committee shall report to the Sustainable Development Committee and the Board of Directors at least once a year and accept the supervision and guidance of the Board of Directors.
Strategy
To implement a company-wide tracking and monitoring mechanism, the company uses different scenarios for the two risk types—transformation and entity risks—such as RCP 8.5, IEASTEPS, IEAAPS, and IEANZE, to assess the impact on the company's value chain and specific financial shocks.
In accordance with its risk management policies and procedures, the Company conducts risk identification, analysis, measurement, and response procedures for relevant risks and opportunities at least once a year. Starting in 2023, the Company began identifying climate-related risks and opportunities, and implemented risk management based on their probability of occurrence and impact, aiming to control risks within a tolerable range as much as possible. The Company's definition of probability of occurrence is: short-term (within three years, 2024-2026), medium-term (three to five years, 2027-2028), and long-term (more than five years, 2029-2031). To reduce the financial impact of risks and opportunities, the Company will establish risk and management mechanisms and strengthen their connection with financial information, aiming to proactively plan for corresponding contingency capabilities.
Short-, medium-, and long-term risks and opportunities
| Short term |
Risk |
|
| Chance |
|
|
| Mid-term |
Risk |
|
| Chance |
|
|
| Long-term |
Risk |
|
| Chance |
|
Risk Management
In response to the aforementioned short-, medium-, and long-term risks and opportunities, the Company has established an identification process and a comprehensive management procedure for risks and opportunities.
Climate Risk and Opportunity Identification Process
| 1.Gather information on climate risks and opportunities. | We conduct thorough research into global climate change trends and issues of concern relevant to our industry. This includes past and projected climate change, policy and legal changes, market trends, and technological developments, all of which have potential impacts on our business and finances. |
| 2. Identify the risks and opportunities of the entity and transformation. |
Through interviews with various departments, we compiled a list of all climate risks and opportunities that could potentially impact our operations, and designed a climate change risk and opportunity assessment questionnaire accordingly. This questionnaire assesses the specific impact of these climate-related trends and issues on our business, including identifying potential risks to our physical assets, supply chain, operations, and market position, as well as identifying potential transformation opportunities. |
| 3. Analysis of financial shocks |
In accordance with TCFD guidelines, we will make corresponding financial disclosures to clarify our understanding and response to climate change-related risks and opportunities. This will include disclosing the extent of the financial impact on the Company, its risk management strategies and objectives, and its risk and opportunity outlook over different timeframes. Through these financial disclosures, we will provide stakeholders with greater transparency regarding the Company's climate-related risk management. |
| 4. Develop countermeasures |
For the key risks and opportunities we identify, we will propose corresponding countermeasures. These measures aim to effectively address potential risks and fully leverage opportunities to achieve business objectives. Simultaneously, we will regularly review and evaluate management effectiveness, understand the implementation status and specific results of these countermeasures, and make necessary rolling adjustments in a timely manner. |
| Financial impact |
Risks and opportunities |
||||
| Almost never(1point) | Unlikely (2points) |
Possibly (3points) |
Very likely (4points) |
Almost certainly (5points) | |
| It never happened. |
It hasn't happened in 10 years. | It may happen more than once within 10 years |
It may happen multiple times within 10 years |
It will definitely happen |
|
|
High (5 points)
|
❶
|
❸❹
|
|
|
|
|
Intermediate to high (4 points)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Medium (3 points)
|
❷
|
|
|
|
|
|
Low to medium (2 points)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Low (1 point)
|
|
|
|
|
|
15-25 points: Significant risk/opportunity ; 6-14 points: Medium risk/opportunity; 1-5 points: Low risk/opportunity
Transformation risks
| Risk aspect |
Risk events and descriptions |
Timing, probability, and extent of impact Potential financial |
Potential financial impact |
Response measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ❶ Policies and regulations |
Increase greenhouse gas emission pricing Taiwan's Climate Change Response Act was passed in 2023, including provisions for carbon fees. Initially, the provisions for large carbon emitters and electricity consumers will be prioritized. The Ministry of Environment will begin targeting companies with annual carbon emissions exceeding 2.5 trillion kcal/kg starting in 2025. A carbon fee will be levied on every 10,000 metric tons, and the scope of collection will be gradually expanded in the future. |
Period of occurrence: Middle Probability of occurrence: High Impact level: High |
Increase operating costs |
- Set proactive carbon reduction targets and regularly track the effectiveness of these reductions. - Map the company-wide net-zero emissions path, develop net-zero strategies, and regularly track their effectiveness. |
| ❷ Policies and regulations |
Strengthen the obligation to report emissions - In 2022, the Financial Supervisory Commission (FSC) announced that listed companies with capital of less than NT$5 billion must complete greenhouse gas inventory checks for their subsidiaries in the consolidated financial statements by 2027 and complete verification by 2029, thus expanding the scope of greenhouse gas inventory checks and verification. - The stock exchange mandates that companies disclose ESG-related information, covering topics such as greenhouse gas emissions, energy management, water resources, waste, human development, and board and investor communications. - The customer requires all its suppliers to provide information on greenhouse gas emissions. |
Duration: Short-term Probability of occurrence: High Impact level: Medium |
Increase operating costs - Increased costs of inspection and verification |
By identifying emission hotspots through greenhouse gas inventory, early planning of reduction measures can lower the cost of greenhouse gas emissions. |
| ❸ Technology |
- he transition costs of replacing existing products and services with low-carbon goods. - The company uses energy-saving and efficiency-enhancing process equipment or peripheral equipment for product manufacturing. |
Period of occurrence: Middle Likelihood of occurrence: Medium to high Impact level: High |
Increase operating costs - Increased R&D expenses - Increased costs of raw materials, equipment, and procurement |
Upgrade existing energy equipment, such as replacing it with energy-efficient devices or adopting renewable energy sources. Simultaneously evaluate the implementation of new technologies and innovation strategies to reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency. |
| ❹ Market |
Changes in customer behavior International net-zero carbon emission trends and regulations and policies in various countries increase client-side demand. Uncertainty in upstream and downstream supply chain layout, or customer priority Companies that choose low-carbon production must therefore invest in research and development. Explore more emerging green energy technologies. |
Duration of occurrence: Long-term Likelihood of occurrence: Medium to high Impact level: High |
Reduced revenue Increase operating costs - Increased R&D expenses - Increase procurement costs - Increased cost of acquiring green energy technologies |
-
Review and analyze international net-zero trends and the carbon reduction targets and strategies of major clients, and formulate and implement reduction targets in accordance with the Science-Based Targets Initiative (SBTi). - Invest in the research and development of green products and green processes, and gradually implement green supply chain management. |
|
Rising raw material costs Suppliers must comply with local government carbon emission standards and regulations. The demand requires investment in more low-energy-consuming processes, and the global economy is not yet fully developed. Stability has led to increased inflation and higher electricity costs. |
Duration: Short-term Probability of occurrence: High Impact level: High |
Increase operating costs - Increase procurement costs - Increased energy consumption and carbon credit allocation costs |
We will continue to actively negotiate with suppliers, communicate our sustainable supply chain management strategy and objectives, strengthen supply chain carbon management, and proactively address risks such as stockouts and material shortages. |
Entity risk
AIRZON identifies the potential impact of extreme weather events (typhoons, droughts, and heavy rainfall) on the company's plant facilities, causing damage and logistical difficulties, which could consequently affect the company's operations. Regarding the risks of typhoons and heavy rainfall, Taipei and mainland China are important production bases for Yongdao. Based on the Taiwan Climate Change Projection and Adaptation Knowledge Platform (TCCIP) analysis of the northern region, under the scenarios of the average change rate of the maximum consecutive 5-day rainfall under RCP 6.0 and RCP 8.5, the average change rate of the maximum consecutive 5-day rainfall in northern China under RCP 6.0 is projected to increase by 33% by the end of this century, from the current average of 403 mm to 536 mm; under the RCP 8.5 scenario, it is projected to increase by 36% by the end of this century, from the current average of 403 mm to 548 mm. However, neither plant area is a low-lying area, and according to the International Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Technology Center's 3D Disaster Potential Map, there is no flooding potential in either plant area.
Regarding the drought risk, based on the Taiwan Climate Change Projection and Adaptation Knowledge Platform (TCCIP) analysis of the northern region, under the most severe warming scenario of RCP 8.5 at the end of the century, although the average rate of change of the maximum consecutive days without rainfall in the northern region will increase by 12% by the end of this century, from the current average of 38 days to 42.5 days, according to the World Resources Institute's "Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas," both of our company's plants are located in low-to-medium risk areas, and our company assesses that its significance will not affect the plant's operational processes and production.
| Risk aspect |
Risk events and descriptions |
Likelihood of occurrence and degree of impact | Potential financial impact |
Response measures |
| Immediate |
The severity of extreme weather events such as typhoons and floods has increased. Extreme weather events such as typhoons and floods can cause production disruptions and transportation disruptions. Difficulties in transportation and supply chain disruptions, etc., have damaged the company's operations. |
Duration: Short-term Probability of occurrence: High Impact level: Low |
Increase operating costs/capital expenditures - Plant and equipment expenditures in response to extreme weather - Investment in disaster prevention-related assets |
-
Assess the drought/flood risks in the manufacturing plant area and develop and implement risk mitigation measures.
- Gradually require suppliers to assess the flood and drought risks to their operating facilities, implement relevant disaster mitigation measures, and enforce auditing systems. - The traditional long supply chain is being transformed into a short blockchain to reduce freight distances, lower the risk of natural disasters during transportation, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions during the transportation phase. |
| Long-term |
Extreme rainfall and drought Extreme rainfall and drought events affect reservoir storage capacity, leading to reduced production capacity. Disruptions, transportation difficulties and supply chain disruptions |
Duration: Short-term Probability of occurrence: High Impact level: Low |
Product revenue decreased Increased transportation and energy costs |
Indicators and Targets
Since 2023, our company has established a greenhouse gas inventory standard mechanism in accordance with ISO 14064-1 and the Environmental Protection Administration's Greenhouse Gas Inspection Guidelines, conducting regular annual inventory checks on greenhouse gas emissions from all our plants. In 2025, we committed to joining the Science-Based Emission Reduction Targets Initiative (SBTi), using 2024 as the base year, with targets set for a 63% reduction in total emissions from Category I and II emissions by 2035, and a 66.3% reduction in economic intensity emissions from Category III, Category I goods and services purchased.
Greenhouse gas and other gas emissions:
Unit: metric tons of CO2e
| Project |
2023 | 2024 |
| Category 1: Direct Greenhouse Gas Emissions |
160.65 | 214.09 |
| Category Two: Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions |
3,839.97 | 5,514.70 |
| Category 3 |
- | 51,446.20 |
| Total emissions = Category 1 + Category 2 |
4,000.62 | 5,728.79 |
| Total emissions = Category 1 + Category 2 + Category 3 |
- | 57,174.99 |
| Greenhouse gas emission intensity (Category 1 + 2) |
1.49 | 1.02 |
| Greenhouse gas emission intensity (Category 1 + 2 + 3) |
- | 10.18 |
Note 1: Emissions statistics for 2023 and 2024.
Note 2: Greenhouse gas emission intensity = Total emissions (metric tons of CO2e) / million million tons of revenue; revenue is sourced from the consolidated profit and loss statement of the annual report.
Note 3: The Category III emissions inspection was not carried out in 2023, therefore no relevant data is available for that year.
Note 4: Covers the entire Yongdao Group, including the Taipei Operations Headquarters, Taipei Plant, Yongdao in China, Yongdao in Japan, Yongdao in the United States, and Yongdao in Vietnam.
Note 5: Source: Ministry of Economic Affairs Energy Agency website(https://www.moeaea.gov.tw/)。
The Company has incorporated the progress and achievements of climate-related issues into the annual performance and variable compensation of senior managers, and disclosed relevant governance and implementation results in accordance with the TCFD framework, in order to continuously strengthen the integration of climate issues into operations management and decision-making.
TCFD Disclosure Comparison Table
| Face |
TCFD Recommends Disclosing Projects | Sustainability Report Corresponding Chapter |
page number |
| governance |
- How does the board oversee climate-related issues? - How management assesses and manages climate-related issues |
4.1 Climate Change Response (TCFD) | 87 |
| Strategy |
- Short-, medium-, and long-term climate-related risks and opportunities identified by the company - The impact of climate-related issues on companies' business models, strategies, and financial planning. - Scenario analysis (including scenarios with a temperature of 2°C or higher) |
Short-, medium-, and long-term risks and opportunities |
88 |
| Risk Management |
- Identification and assessment process for climate-related risks - Management process for climate-related risks - Explain how the above-described risk identification and management process is integrated into the company's overall risk management system. |
Identification of climate-related risks and opportunities |
88 89 90 |
| Indicators and Target |
- Whether the evaluation metrics are consistent with the company's strategy and risk management - Disclosure of greenhouse gas emissions and related risks in Categories I, II and III (if applicable) - Management objectives and related performance |
Indicators and Targets Carbon Fee/Carbon Tax Scenario Analysis |
91 92 |